Please wait...
About This Project
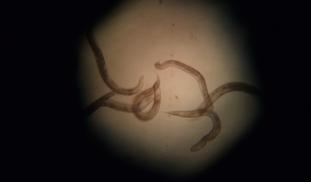
The hypothesis that is being tested is if C. elegans will build up amyloid beta (AB) plaques after heat stress exposure, possibly leading to Alzheimer's disease (AD). C. elegans (nematodes) demonstrate symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease such as amyloid plaques, genes and their mutations, and memory impairments. Heat-shock is a form of stress that could potentially increase the rate of AD, and during heat shock, transcription and translation proteins in C. elegans will become inhibited.