90
0
0
Like?
Please wait...
About This Project
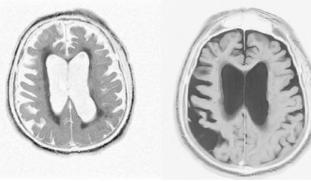
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is associated with prion-like aggregation of the β-amyloid and Tau proteins, that form neurotoxic aggregates in the brain. Studies have pointed out the association between brain-localized bacteria and AD; however. Recently, we identified that bacterial DNA can aggregate Tau protein (Tetz et a, 2020). We will explore whether DNA from brain-localized bacteria triggers β-amyloid misfolding; thus, being, a previously overlooked cause of AD.