Please wait...
About This Project
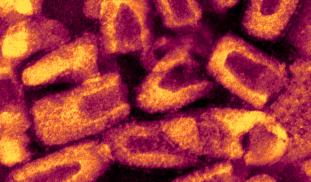
Rabies infection is almost always fatal in humans. The current treatment for a bite from a rabid animal (injection of human serum from immunized people) is often in short supply, especially in developing world settings. We aim to find antibodies from a rabies-vaccinated donor, using blood taken just weeks after vaccination. By sequencing the antibody genes present in these cells, we can make antibodies, providing less expensive and readily available treatment for the virus.

Browse Other Projects on Experiment
Related Projects
Shutting down cancer’s recycling system with exosome-based therapy
Pancreatic cancer is one of the deadliest cancers because its cells survive by recycling their own components...
Developing a novel oxysterol antibiotic to combat drug-resistant tuberculosis
Drug-resistant tuberculosis (TB) is a consistently growing threat to global health. We have developed Oxy291...
Tote-Size portable incubator for rapid field work
Waiting for lab results is slowing science down! We are designing a fully open source portable incubator...