40
0
0
Like?
Please wait...
About This Project
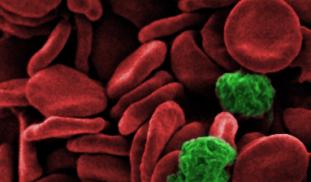
During a malaria infection, parasites sneakily reside inside human red blood cells. They need to make their host cell surface sticky, in order to avoid being filtered out by the spleen. Our goal is to understand the biochemical details of how malaria parasites remodel the red blood cell surface.

Browse Other Projects on Experiment
Related Projects
Coupling of microbial carbon capture and utilization (microCCU) and direct air capture (DAC)
Reducing atmospheric CO2 is critical to mitigating climate change, and negative emission technologies (NETs...
Enhancing Carbon Sequestration By Improving Photosynthetic Efficiency
Enhancing photosynthesis can help mitigate greenhouse gases, but plants and algae use only visible light...
Copper gene-switch for controllable gene expression in plants
Chemical-induced promoters or "Gene Switches" allow expressing a gene of interest in a controllable manner...